Remote Development
Remote Development lets you edit code on a remote server while running Zed locally. The UI stays responsive because it runs on your machine, while language servers, tasks, and terminals run on the server.
For day-to-day workflows, pair remote development with Tasks, Terminal, and Debugger.
Overview
Remote development requires two computers, your local machine that runs the Zed UI and the remote server which runs a Zed headless server. The two communicate over SSH, so you will need to be able to SSH from your local machine into the remote server to use this feature.
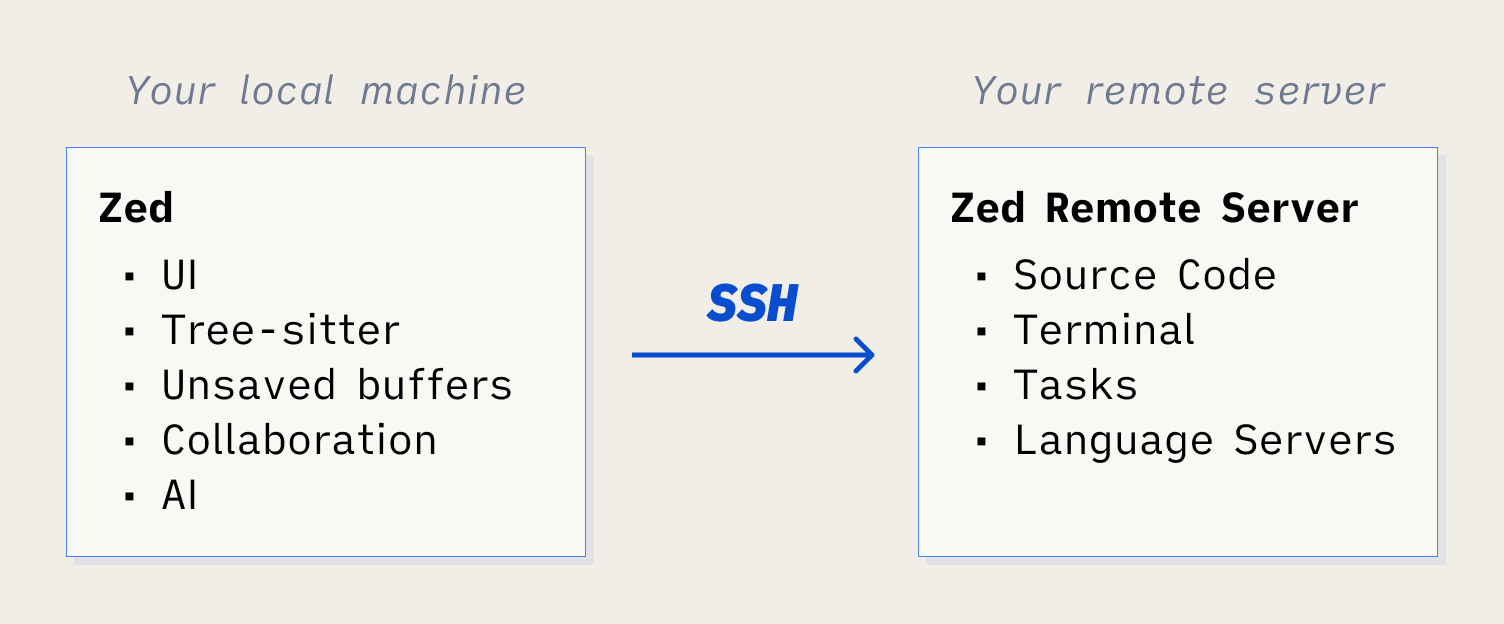
On your local machine, Zed runs its UI, talks to language models, uses Tree-sitter to parse and syntax-highlight code, and store unsaved changes and recent projects. The source code, language servers, tasks, and the terminal all run on the remote server. AI features work in remote sessions, including the Agent Panel and Inline Assistant.
Note: The original version of remote development sent traffic via Zed's servers. As of Zed v0.157 you can no-longer use that mode.
Setup
- Download and install the latest Zed. You need at least Zed v0.159.
- Use ctrl-cmd-shift-o|alt-ctrl-shift-o to open the "Remote Projects" dialog.
- Click "Connect New Server" and enter the command you use to SSH into the server. See Supported SSH options for options you can pass.
- Your local machine will attempt to connect to the remote server using the
sshbinary on your path. Assuming the connection is successful, Zed will download the server on the remote host and start it. - Once the Zed server is running, you will be prompted to choose a path to open on the remote server.
Note: Zed does not currently handle opening very large directories (for example,
/or~that may have >100,000 files) very well. We are working on improving this, but suggest in the meantime opening only specific projects, or subfolders of very large mono-repos.
For simple cases where you don't need any SSH arguments, you can run zed ssh://[<user>@]<host>[:<port>]/<path> to open a remote folder/file directly. If you'd like to hotlink into an SSH project, use a link of the format: zed://ssh/[<user>@]<host>[:<port>]/<path>.
Supported platforms
The remote machine must be able to run Zed's server. The following platforms should work, though note that we have not exhaustively tested every Linux distribution:
- macOS Catalina or later (Intel or Apple Silicon)
- Linux (x86_64 or arm64, we do not yet support 32-bit platforms)
- Windows is not yet supported as a remote server, but Windows can be used as a local machine to connect to remote servers.
Configuration
The list of remote servers is stored in your settings file cmd-,|ctrl-,. You can edit this list using the Remote Projects dialog ctrl-cmd-shift-o|alt-ctrl-shift-o, which provides some robustness - for example it checks that the connection can be established before writing it to the settings file.
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"projects": [{ "paths": ["~/code/zed/zed"] }]
}
]
}
Zed shells out to the ssh on your path, and so it will inherit any configuration you have in ~/.ssh/config for the given host. That said, if you need to override anything you can configure the following additional options on each connection:
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"projects": [{ "paths": ["~/code/zed/zed"] }],
// any argument to pass to the ssh master process
"args": ["-i", "~/.ssh/work_id_file"],
"port": 22, // defaults to 22
// defaults to your username on your local machine
"username": "me"
}
]
}
There are two additional Zed-specific options per connection, upload_binary_over_ssh and nickname:
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"projects": [{ "paths": ["~/code/zed/zed"] }],
// by default Zed will download the server binary from the internet on the remote.
// When this is true, it'll be downloaded to your laptop and uploaded over SSH.
// This is useful when your remote server has restricted internet access.
"upload_binary_over_ssh": true,
// Shown in the Zed UI to help distinguish multiple hosts.
"nickname": "lil-linux"
}
]
}
If you use the command line to open a connection to a host by doing zed ssh://192.168.1.10/~/.vimrc, then extra options are read from your settings file by finding the first connection that matches the host/username/port of the URL on the command line.
Additionally it's worth noting that while you can pass a password on the command line zed ssh://user:password@host/~, we do not support writing a password to your settings file. If you're connecting repeatedly to the same host, you should configure key-based authentication.
Remote Development on Windows (SSH)
Zed on Windows supports SSH remoting and will prompt for credentials when needed.
If you encounter authentication issues, confirm that your SSH key agent is running (e.g., ssh-agent or your Git client's agent) and that ssh.exe is on PATH.
Troubleshooting SSH on Windows
When prompted for credentials, use the graphical askpass dialog. If it doesn't appear, check for credential manager conflicts and that GUI prompts aren't blocked by your terminal.
WSL Support
Zed supports opening folders inside of WSL natively on Windows.
Opening a local folder in WSL
To open a local folder inside a WSL container, use the projects: open in wsl action and select the folder you want to open. You will be presented with a list of available WSL distributions to open the folder in.
Opening a folder already in WSL
To open a folder that's already located inside of a WSL container, use the projects: open wsl action and select the WSL distribution. The distribution will be added to the Remote Projects window where you will be able to open the folder.
Port forwarding
If you'd like to be able to connect to ports on your remote server from your local machine, you can configure port forwarding in your settings file. This is particularly useful for developing websites so you can load the site in your browser while working.
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"port_forwards": [{ "local_port": 8080, "remote_port": 80 }]
}
]
}
This will cause requests from your local machine to localhost:8080 to be forwarded to the remote machine's port 80. Under the hood this uses the -L argument to ssh.
By default these ports are bound to localhost, so other computers in the same network as your development machine cannot access them. You can set the local_host to bind to a different interface, for example, 0.0.0.0 will bind to all local interfaces.
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"port_forwards": [
{
"local_port": 8080,
"remote_port": 80,
"local_host": "0.0.0.0"
}
]
}
]
}
These ports also default to the localhost interface on the remote host. If you need to change this, you can also set the remote host:
{
"ssh_connections": [
{
"host": "192.168.1.10",
"port_forwards": [
{
"local_port": 8080,
"remote_port": 80,
"remote_host": "docker-host"
}
]
}
]
}
Zed settings
When opening a remote project there are three relevant settings locations:
- The local Zed settings (in
~/.zed/settings.jsonon macOS or~/.config/zed/settings.jsonon Linux) on your local machine. - The server Zed settings (in the same place) on the remote server.
- The project settings (in
.zed/settings.jsonor.editorconfigof your project)
Both the local Zed and the server Zed read the project settings, but they are not aware of the other's main settings file.
Which settings file you should use depends on the kind of setting you want to make:
- Project settings should be used for things that affect the project: indentation settings, which formatter / language server to use, etc.
- Server settings should be used for things that affect the server: paths to language servers, proxy settings, etc.
- Local settings should be used for things that affect the UI: font size, etc.
In addition any extensions you have installed locally will be propagated to the remote server. This means that language servers, etc. will run correctly.
Proxy Configuration
The remote server will not use your local machine's proxy configuration because they may be under different network policies. If your remote server requires a proxy to access the internet, you must configure it on the remote server itself.
In most cases, your remote server will already have proxy environment variables configured. Zed will automatically use them when downloading language servers, communicating with LLM models, etc.
If needed, you can set these environment variables in the server's shell configuration (e.g., ~/.bashrc):
export http_proxy="http://proxy.example.com:8080"
export https_proxy="http://proxy.example.com:8080"
export no_proxy="localhost,127.0.0.1"
Alternatively, you can configure the proxy in the remote machine's ~/.config/zed/settings.json (Linux) or ~/.zed/settings.json (macOS):
{
"proxy": "http://proxy.example.com:8080"
}
See the proxy documentation for supported proxy types and additional configuration options.
Initializing the remote server
Once you provide the SSH options, Zed shells out to ssh on your local machine to create a ControlMaster connection with the options you provide.
Any prompts that SSH needs will be shown in the UI, so you can verify host keys, type key passwords, etc.
Once the master connection is established, Zed will check to see if the remote server binary is present in ~/.zed_server on the remote, and that its version matches the current version of Zed that you're using.
If it is not there or the version mismatches, Zed will try to download the latest version. By default, it will download from https://zed.dev directly, but if you set: {"upload_binary_over_ssh":true} in your settings for that server, it will download the binary to your local machine and then upload it to the remote server.
If you'd like to maintain the server binary yourself you can. You can either download our prebuilt versions from GitHub, or build your own with cargo build -p remote_server --release. If you do this, you must upload it to ~/.zed_server/zed-remote-server-{RELEASE_CHANNEL}-{VERSION} on the server, for example ~/.zed_server/zed-remote-server-stable-0.217.3+stable.105.80433cb239e868271457ac376673a5f75bc4adb1. The version must exactly match the version of Zed itself you are using.
Maintaining the SSH connection
Once the server is initialized. Zed will create new SSH connections (reusing the existing ControlMaster) to run the remote development server.
Each connection tries to run the development server in proxy mode. This mode will start the daemon if it is not running, and reconnect to it if it is. This way when your connection drops and is restarted, you can continue to work without interruption.
In the case that reconnecting fails, the daemon will not be re-used. That said, unsaved changes are by default persisted locally, so that you do not lose work. You can always reconnect to the project at a later date and Zed will restore unsaved changes.
If you are struggling with connection issues, you should be able to see more information in the Zed log cmd-shift-p Open Log. If you are seeing things that are unexpected, please file a GitHub issue or reach out in the #remoting-feedback channel in the Zed Discord.
Supported SSH Options
Under the hood, Zed shells out to the ssh binary to connect to the remote server. We create one SSH control master per project, and then use that to multiplex SSH connections for the Zed protocol itself, any terminals you open and tasks you run. We read settings from your SSH config file, but if you want to specify additional options to the SSH control master you can configure Zed to set them.
When typing in the "Connect New Server" dialog, you can use bash-style quoting to pass options containing a space. Once you have created a server it will be added to the "ssh_connections": [] array in your settings file. You can edit the settings file directly to make changes to SSH connections.
Supported options:
-p/-l- these are equivalent to passing the port and the username in the host string.-L/-Rfor port forwarding-i- to use a specific key file-o- to set custom options-J/-w- to proxy the SSH connection-Ffor specifying anssh_config- And also...
-4,-6,-A,-B,-C,-D,-I,-K,-P,-X,-Y,-a,-b,-c,-i,-k,-l,-m,-o,-p,-w,-x,-y
Note that we deliberately disallow some options (for example -t or -T) that Zed will set for you.
Known Limitations
- You can't open files from the remote Terminal by typing the
zedcommand.
Feedback
Please join the #remoting-feedback channel in the Zed Discord.
See also
- Running & Testing: Run tasks, terminal commands, and debugger sessions while you work remotely.
- Configuring Zed: Manage shared and project settings,
including
.zed/settings.json. - Agent Panel: Use AI workflows in remote projects.
- Remote Development on zed.dev: Product overview and release updates.